The ongoing battle between AMD’s Ryzen 7 1800X and Intel’s Core i7 series has fueled countless debates within the computing community. Each processor has its own set of strengths, weaknesses, and devoted followers. For anyone looking to build a high-performance PC in 2024, deciphering which one reigns supreme requires a deep dive into their core architecture, performance capabilities, and market reception. This article aims to provide just that—a thorough, engaging exploration that showcases what each has to offer and helps you make an informed decision.
Table of Contents
- Head-to-Head Comparison
- Technological Evolution
- Performance Powerhouses
- Market Dynamics
- Future Prospects and Conclusion
Head-to-Head Comparison
To start, a direct comparison between the AMD Ryzen 7 1800X and Intel Core i7 highlights divergent paths rooted in design philosophies and targeted segments.
AMD Ryzen 7 1800X:
- Cores/Threads: 8 cores, 16 threads
- Base/Boost Clock: 3.6 GHz / 4.0 GHz
- Process Technology: 14nm
Intel Core i7:
- Typical Configurations: 4 to 8 cores, 8 to 16 threads depending on the generation
-
Core Attributes:
- Models like the i7-7700K focus on single-core performance with higher boost clocks reaching up to 4.5 GHz.
- More recent iterations such as the i7-13700K offer similar core/thread counts to the Ryzen 7 1800X but incorporate Intel’s advances in process technology and architecture.
Pros and Cons
Ryzen’s Strengths:
- Multi-Core Performance: The Ryzen 7 1800X’s architecture excels in multi-threaded tasks like rendering and content creation.
- Cost Efficiency: Historically, AMD has provided compelling price-to-performance ratios, making Ryzen a favorite among cost-conscious consumers.
Intel’s Strengths:
- Single-Core Superiority: Intel’s chips often have an advantage in single-threaded tasks and gaming scenarios, delivering higher frames per second due to higher IPC (Instructions Per Clock).
- Established Market Presence: Long-standing dominance has led to widespread compatibility and software optimization for Intel CPUs.
Technological Evolution
Both AMD and Intel have undergone significant advancements since the debut of these processors. The AMD Ryzen 7 1800X emerged as a challenger to Intel’s dominance, leveraging the Zen architecture to focus on parallel processing efficiency and energy management, thanks to its 14nm manufacturing process. These advancements reshaped AMD’s market position, closing performance gaps and reshaping consumer perceptions.
Intel, unwilling to cede ground, refined their process technology to improve power efficiency with each successive generation. Their move towards hybrid architectures, incorporating high-performance and efficiency cores, represents a response to market demands for flexibility across workloads. The core differentiation stems from single-core performance due to advanced features like Turbo Boost, which propels Intel to higher peak speeds.
Performance Powerhouses
The performance battle between Ryzen 7 1800X and Intel i7 is nuanced:
Gaming Benchmarks
Gaming has traditionally favored Intel’s architecture due to its robust single-thread performance. Games that leverage few cores run faster on Intel CPUs, a factor critical for gamers. Illustrated by benchmarks, Intel’s processors often reach higher FPS rates in competitive gaming scenarios, underscoring their single-core prowess.
Productivity and Content Creation
Where AMD’s Ryzen truly shines is in productivity tasks. The 1800X efficiently utilizes all available threads, offering superior performance in multi-threaded applications like 3D rendering and video encoding. This efficiency is critical for professionals whose workloads demand multi-threaded capabilities, delivering tangible performance enhancements in real-world tasks.
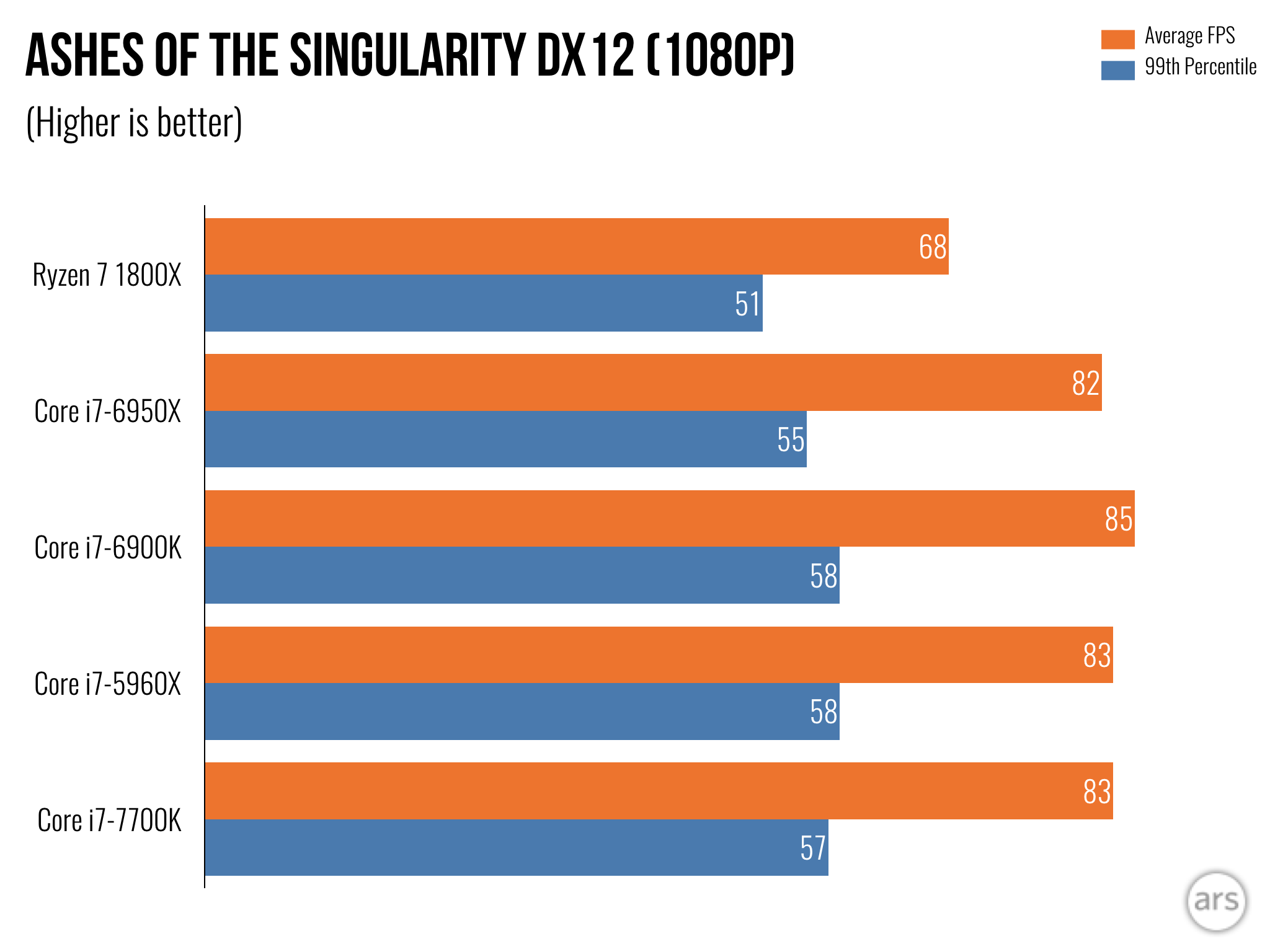
Market Dynamics
Current Trends:
- Consumer Preferences: Reflect a balanced market where AMD’s aggressive pricing strategies and superior multi-threaded performance gained traction among multi-taskers and content creators. Conversely, Intel’s consistent single-thread edge ensures dominance in gaming markets.
- Pricing Models: AMD’s competitive pricing strategy has forced Intel to reevaluate its models, particularly given the rise of AMD processors in custom builds and OEM systems.
Technological Impact:
- AMD: Introduced new generations of Ryzen that continue to focus on IPC improvements, energy efficiency, and core count increases.
- Intel: Responded with advancements in their fabrication tech, pushing the envelope on single-core performance and hybrid core structures, encompassing both high-performance and energy-efficient cores.
Future Prospects and Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing between the AMD Ryzen 7 1800X and an Intel Core i7 hinges on your needs:
- For Multi-Threading and Power Efficiency: Ryzen 7 1800X remains a strong contender for users whose tasks are multi-thread reliant and for those looking for value-oriented solutions.
- For Gaming and Single-Thread Performance: Intel’s offerings generally provide better results, especially in gaming and applications prioritizing single-thread execution.
Both competitors are scripting a fascinating future for computing. AMD’s capacity to innovate and disrupt Intel’s previous monopolized stronghold bodes well for technology enthusiasts. Meanwhile, Intel’s adaptive strategies reflect its endeavors to stay competitive in a landscape enhanced by evolving needs and cutting-edge technological advancements.
The decision ultimately rests on aligning the processor’s strengths with user-specific workloads and scenarios, ensuring optimal performance tailored to individual demands. As innovation accelerates, consumers gain the upper hand in a market defined by choice and tailored solutions.
